Notes from The Five Traditional Process Groups Explained
Original article here
- This is where the project is formally authorized by the sponsor, initial scope defined, and stakeholders identified.
- It is important that the PM is formally authorized at this point, as PMs have a lot of accountability and little authority.
2- Planning
- PMBOK outlines 24 discrete processes involved in planning
- Significant idea is to think through the process in advance
3 - Executing
- Since the project team is important in execution of the process, it is also important that cultivating the team is as well.
4 - Monitor and Control
- One way to think about monitoring and controlling is to imagine that you were driving across the country according to your plan or a roadmap. But if you got lost and you didn't have a GPS you'd stop, ask for directions and get back on track, or maybe based on new information, such as a new road that would cut hours off the trip, you'd change or update your plan.5 - Closing
- The project manager should formally close the project by archiving records, holding a lessons learned session, and celebrating and releasing the team. And the lessons learned along with other historical information should be centrally archived to be used as input to future projects to prevent reinventing the wheel.
- Rigor should be maintained as constant throughout the project, even in closing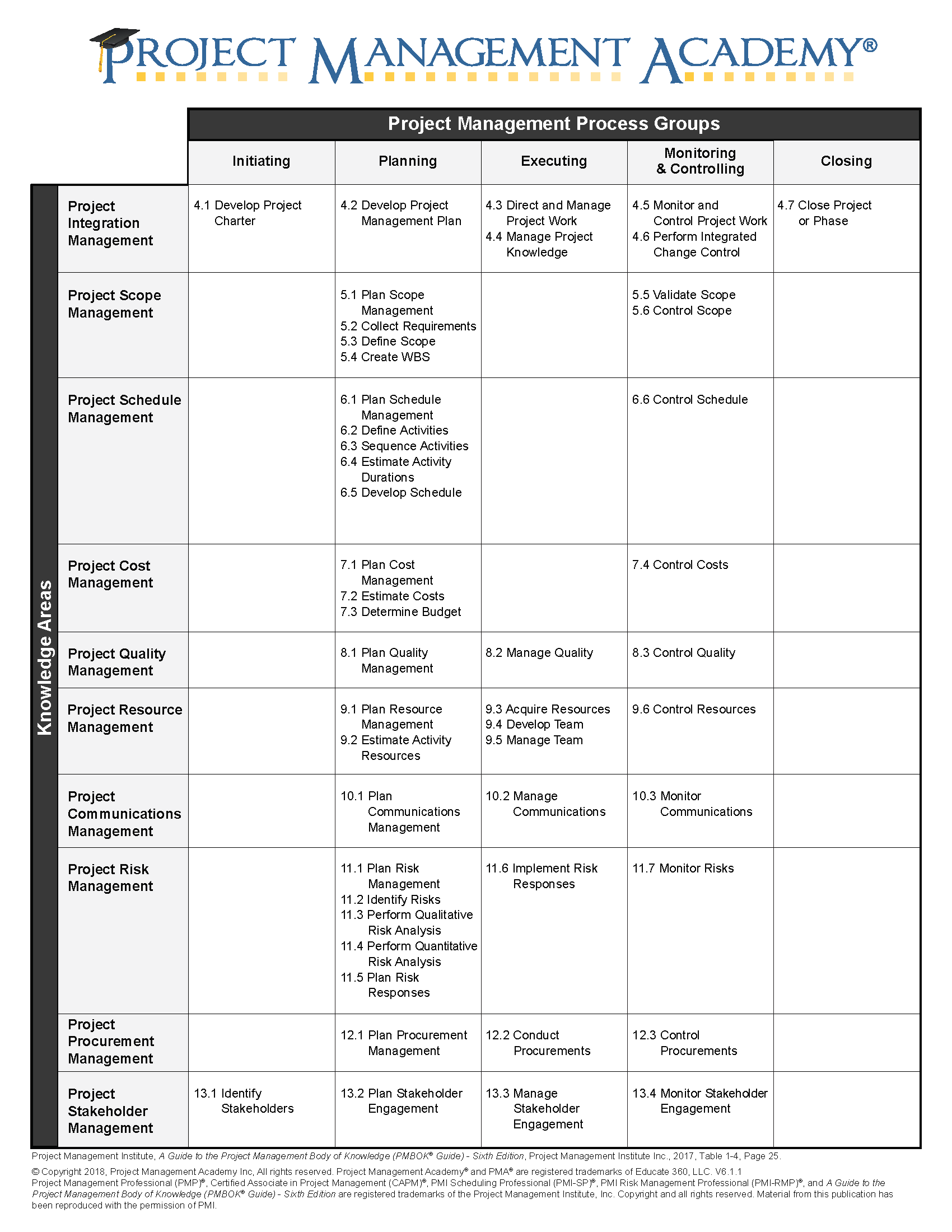
Comments
Post a Comment